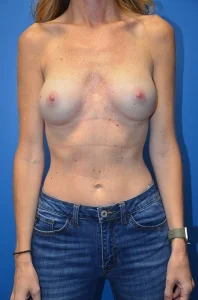
Despite optimal pre-operative planning and a well-executed surgery, there are still occasions when breast implant revision procedures may be necessary. Since the breast has already undergone a previous surgery, a revision can be more complex than the primary procedure. Factors that can make revisional surgery more difficult include scar tissue, altered implant position, thinning of the tissue or skin, and distorted breast shape.
Our board-certified plastic surgeon in Richmond has performed hundreds of breast procedures, including breast augmentations, breast lifts, breast reductions, and complex breast reconstruction surgeries for breast cancer patients. For those in need of a breast revision, Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS utilizes his advanced surgical techniques to tailor surgery according to each patient’s unique needs.
What Is Breast Implant Revision?
Breast implant revision surgery is a procedure to address cosmetic or medical concerns following a previous breast augmentation. Patients may choose to switch to a different breast implant at may develop from aging, weight changes, or hormones; or decide to completely remove their breast implants. Due to the more challenging nature of this surgery, breast implant revision should only be performed by a highly skilled surgeon experienced with this complex procedure.
During your consultation, our plastic surgeon will perform a physical exam and evaluate your complete medical and breast history. Please bring all relevant information to the consultation including implant cards, names and locations of your prior surgeons, and previous medical records. This will assist Dr. Zemmel in diagnosing your issues and formulating a comprehensive treatment plan.
How Soon After Breast Augmentation Can I Get a Revision?
Patients are typically advised to wait at least six months to one year after their original surgery before undergoing a breast revision procedure. The exact timing will depend on your reason for a revision, overall health, individual healing rate, and other factors. To determine the best surgical plan and timing, Dr. Zemmel will complete a thorough examination and discussion of your needs and goals.
What Are Common Reasons for Breast Revision Surgery?
There are a number of reasons women seek breast implant revision surgery. Below are some of the most common causes for revision as well as the general approaches to treatment:
Implant Rupture
All prosthetic body implants have a lifetime including breast implants. Today’s breast implants are considered safe and durable, but with many years of normal usage, rupture will occur.
Saline Implants
Saline implants are filled with saline (salt water) solution and silicone implants are filled with cohesive silicone gel. If a saline implant ruptures, the saline solution flows out of the implant and is harmlessly absorbed by the body. The implant and breast will deflate over a short period of time alerting the patient of the need for replacement. The rupture rate for newer saline implants is approximately 1.8% per year.
Silicone Implants
Fourth generation cohesive silicone implants have a rupture rate of approximately 1% at 6 years. If a cohesive silicone gel implant ruptures, there is theoretically little change in shape of the breast, and the implant is said to rupture “silently.” The FDA therefore recommends a schedule of periodic breast MRIs to evaluate the implant for rupture. The chance of gel leakage or migration is very low with cohesive gel implants. Older generation silicone implants have a significantly higher rupture rate and are often found to be ruptured on re-exploration. Depending on the severity of leakage complete, capsulectomy may be required.
In the event of a saline or silicone rupture, Dr. Zemmel recommends replacement. He usually replaces both implants at the same time, and if applicable, our staff will discuss any warranty issued by the original manufacturer. These issues will be discussed at length with you during your consultation.
Breast Implant Exchange
A revision surgery to replace breast implants — known as breast implant exchange — is designed to replace current implants for a different size, material (silicone or saline), or profile (projection forward from the chest wall). One of the most common reasons for breast implant exchange tends to be switching from saline to silicone breast implants, as silicone is well-known for its more natural look, shape, and feel, and reduced chance of rippling. A breast implant exchange may also be performed if a complication with the current implants has occurred, such as an implant rupture.
Change Implant Size
Breast augmentation usually has a very high post-operative satisfaction rate. However, breasts may age and change in shape and consistency; therefore, many women desire changes in their breast size. Many women may wish to go somewhat larger while others might prefer a smaller breast size.
Increasing Breast Implant Size
For women that want to increase the size of their breasts, this can be achieved by increasing the size of the implant. Your surgeon will measure your breasts and help you decide the final size that is right for you. To get the most natural-looking result, Dr. Zemmel typically recommends an implant size that provides a well-proportioned, balanced outcome. Therefore, he does not recommend extremely large implants, as the complication rate is higher with these implants. Treatment usually consists of reopening of the breast, removal of the old implants, increasing the size of the pocket by opening the capsule, and placement of the new implants.
Decreasing Breast Implant Size
Decreasing the size of an implant requires careful pre-operative planning. A significant size decrease can cause deflation of the breast and increased ptosis (sagging) of the nipple and areola. Decreasing the volume of the implant causes a simultaneous decrease of the diameter of the implant. The original breast implant pocket may therefore require capsulorrhaphy, or suturing of the capsule and pocket to close down the space. A mastopexy (breast lift) may also be necessary to achieve optimum shape and nipple position.
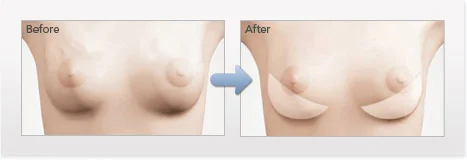
Treatment of Rippling
*Individual Results May Vary
Rippling of a breast implant is when folding of the breast implants becomes visible beneath the skin and breast tissue. There are several factors that may increase the risk of rippling. Thin women with thin skin and little breast tissue are at a higher risk of rippling. As a general principle, the thinner the overlying soft tissue covering the implant, the higher the risk of feeling and seeing the implant beneath the soft tissue covering. Saline implants have a higher risk of rippling than silicone gel implants, and subglandular implants (over the muscle) have a higher risk than submuscular (under the muscle) or dual plane implants. Additionally, under-filling a saline implant can cause the edges of the implant to become wavy.
Dr. Zemmel is the best doctor in Richmond! His kindness and compassion accompanied by his amazing skill puts him leaps and bounds above the rest! His staff is wonderful! There is no better than this practice!!!;
HairBy Andie
January 16, 2018
Implant Malposition
The optimal shape of the breast occurs when the breast implant is located directly beneath the breast and the nipple-areola position is directly over the most forward projecting part of the dome of the implant. Implant malposition occurs when the implant is not located in this position, such as the following circumstances:
- High implants occur when the breast implant fails to drop over the first few months after surgery. A number of factors may lead to this, including incomplete pectoralis major muscle division, an undiagnosed elevated inframammary fold, or capsular contracture. Treatment may require surgical revision to lower the implant and remove the capsular contracture.
- Symmastia occurs when the cleavage between the breasts is obliterated, giving the appearance of a single breast. This is also known as a “uniboob.” Symmastia can be caused by a number of factors, including complete medial pectoral muscle release, placement of too large of an implant, and over-dissection of the inner aspect of a subglandular breast pocket. Correction of symmastia requires recreating the medial fold and cleavage between the two breasts. This can be done with a pocket reassignment from the subglandular to submuscular pockets and suture placement.
- Lateral displacement of implants occurs when the implant pockets are too far apart, causing the implants to shift to the side of the chest wall or to the underarm areas when lying. This is usually caused by over-dissection of the outer aspect of the breast pocket during original implant placement. Treatment usually requires surgical re-exploration and placing sutures in the outer aspect of the breast pocket to close down the lateral pocket causing the implant to shift centrally. Replacement with a smaller implant may also be necessary.
- Low positioning of the implants, or bottoming out, is caused when the implants descend to an abnormally low position on the chest wall. Typically, the implant descends beneath the level of the inframammary fold. This shifts the volume of the implant lower. The lower hemisphere of the breast may appear stretched, and the nipple areola may appear abnormally high on the breast. Bottoming out may occur when the inframammary fold is lowered too aggressively in surgery or by stretching of the lower pole skin of the breast. It may occur in one or both breasts. Treatment usually requires surgical re-exploration and raising the level of the inframammary crease with sutures.
Dr. Zemmel performs several newer techniques to correct implant malposition. These incorporate the older methods of capsulotomy and capsulectomy (removal of the breast capsule), capsulorrhaphy (suturing the capsule), and pocket reassignment from the subglandular to submuscular position. OurDr. Zemmel combines these techniques with the use of acellular dermal matrix (Alloderm) to reinforce the capsule repairs. This gives additional tissue thickness and soft tissue strength. The reformation of capsular contracture may also be reduced.
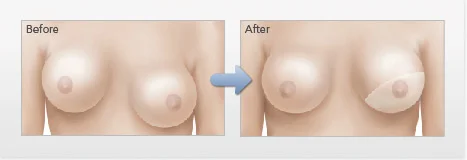
Capsular Contracture
Many different artificial materials have been used to create prosthetic implants. Prosthetic implants are in use for joint replacement of the knees, shoulders, and hips. Plates and screws are used to repair bones. Breast implants are constructed of silicone rubber shells containing either saline solution or cohesive silicone gel as the filler materials. When a prosthetic implant is placed, the body heals around the implants and gains “tolerance” to the new device. Many materials have been developed that are tissue compatible.
Usually a thin wall of soft tissue forms directly around the implant to serve as the interface between the implant and the body. This is called the capsule. In rare cases the capsule becomes thickened and firm, and distortion of the shape of the implant and tenderness of the breast can occur. Capsular contracture can be divided into grades 1, 2, 3, and 4, with grade 4 being the most severe. Over time, the implant tends to become rounder, and the forces of contracture pull the implant in an upward sideways direction. Occasionally, the overlying skin and soft tissue can become thin and distressed.
*Individual Results May Vary
Severe capsular contracture is usually addressed surgically and is corrected in the most severe cases. The treatment plan may consist of:
- Complete removal of the implants
- Replacement of the implants
- Changing from saline to silicone implants
- Capsulotomy (incising the capsule)
- Capsulectomy (complete removal of the capsule)
- Pocket reassignment (changing from subglandular to submuscular)
The surgical treatment of capsular is complex, and your surgeon will discuss all of the available options with you.
Schedule Your Breast Revision Consultation
For more information on breast augmentation revision options, or if you would like to schedule a consultation here at our practice, please contact Richmond Aesthetic Surgery.